Please Die, You Dying Babies, in My Diarrhea.
Despite being treatable and preventable, i.vi million people died from diarrheal diseases in 2017; i-tertiary were children nether five years old. This makes it i of the largest killers of children. Here we await at where and why children are dying from diarrrheal diseases, and what we can do stop this.
Diarrheal diseases are i of the biggest killers of children worldwide
In 2017, most i.six one thousand thousand people died from diarrheal diseases globally.
This is more than all deaths from all 'intentional injuries' combined in the same year: near 800,000 died from suicide, 405,000 from homicide, 130,000 in conflict, and 26,500 from terrorism – in full 1,355,000.ane
Equally the visualization shows, one-third of all who died from diarrheal diseases were children under five years old. For most of the by three decades nether-5s have accounted for the majority of deaths from diarrheal diseases – dorsum in 1990 it killed i.seven million children.
Diarrheal disease was the crusade of every tenth child's death in 2017 – more than half a million of the five.iv million children that died in 2017 died from diarrheal affliction.
Diarrheal diseases are the third leading cause of kid mortality globally, falling just backside pneumonia and preterm birth complications.
Where are children dying from diarrheal diseases?
The decease rate from diarrheal diseases is highest in the globe's poorest countries: this chart shows the relationship between the death charge per unit from diarrheal diseases and the country's average income.
The death rate from diarrheal diseases in many of the poorest countries is higher than 100 annual deaths per 100,000 children. In those countries with the worst health – including Madagascar, Chad and the Key African Commonwealth – the rate is higher than 300 per 100,000.
In high-income countries the expiry rate is very low. In many European countries, but also some rich Asian countries the rate is below one per 100,000 per twelvemonth.
At lower levels of income risk factors for diarrheal diseases such as lack of access to clean water, rotavirus vaccine availability, undernutrition, stunting and others are the most prevalent.2
What causes diarrheal diseases in children?
Agreement the cause of illness is important so that nosotros can set our priorities on the interventions and treatments that would save most lives, e.grand. developing vaccines confronting the main agents for diarrhea and using antibiotic treatments only when they are appropriate.
Diarrheal diseases are caused primarily past viral and bacterial pathogens. The visualization shows the major pathogens responsible for diarrhea in children; the area of each box corresponds to the number of deaths from diarrhea in 2016 that can exist attributed to each pathogen.
While bacterial pathogens (shown in blood-red) are the major group of organisms responsible for diarrheal diseases, rotavirus is the single largest causative amanuensis.3
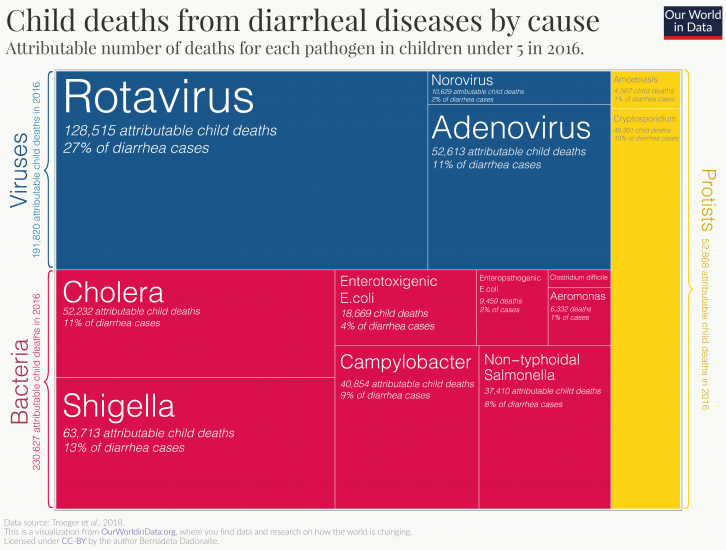
Why are children nevertheless dying from diarrhea?
There are two main reasons why the number of children dying from diarrhea is still then large – the prevalence of diarrhea-associated risk factors and the lack of admission to essential handling.
The figure shows the number of deaths associated with the major risks factors for diarrheal diseases: unsafe drinking water, poor sanitation and malnutrition are responsible for the largest portion of deaths.
Since 1990 nosotros have made a lot of progress in reducing these major risks; you tin read more in our enquiry entries on Hunger and Undernourishment, Extreme Poverty and Water Use and Sanitation. But continued progress is nevertheless needed.
In improver to reducing exposure to risks factors, increasing access to oral rehydration therapy (ORT), therapeutic zinc use and the coverage of rotavirus vaccines were all shown to be essential for reducing the burden of diarrheal diseases in children.4
How tin we stop child deaths from diarrhea?
Diarrheal diseases are both 'preventable and treatable', equally the WHO says, because we already know how to bargain with many of the take a chance factors that may lead to diarrhea and, if diarrhea cannot be avoided, we know how to treat it.
The table below lists the range of interventions available for the treatment of diarrhea nosotros accept today.5
Some of these interventions, such as ORS, breastfeeding and improvements in sanitation broadly target all-causes of diarrhea, whereas, vaccination and antibody use are specifically directed against the causative agents of the disease.
Water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) interventions are the all-time way to prevent diarrheal diseases. Mitt washing with soap, meliorate h2o quality and better sanitation have been shown to reduce the risk of diarrheal infections by 47%, 17% and 36%, respectively.6
Educating mothers about the importance of breastfeeding is besides of import. Breastfeeding allows for the transfer of maternal amnesty to the child – in developing countries infants that are not breastfed are six times more than likely to die from infectious diseases, such every bit those causing to diarrhea, in the commencement 2 months of their lives.seven
Another way to forestall diarrheal diseases is vaccination. Until relatively recently, there were few vaccines available to prevent diarrheal diseases. Cholera vaccine has been licensed since 1991 but it is primarily given to travelers and used equally an outbreak command mensurate. This is because targeted immunization combined with other sanitary measures is more cost-constructive than immunizing every individual with a vaccine that only provides a few years of protection.8
In 2006, however, new vaccines confronting rotavirus – the leading cause of childhood diarrhea as the treemap above shows – have been introduced. The most recent studies testify that, while the effectiveness of the new rotavirus vaccines vary across different countries, it works well in protecting children against rotavirus illness.9
We volition explore the success, potential and limitations of rotavirus vaccines in an upcoming post.
When preventative measures fail, several options for the treatment of diarrheal diseases are available, including nutritional interventions and antibiotic use when necessary. But the single best treatment for diarrheal diseases is a surprisingly simple mixture of water, salt and sugar: otherwise known as the oral rehydration solution.10
The estimates of ORS effectiveness vary by source, with some suggesting that the current use of ORS helps to preclude 69% of diarrheal deaths and, if its coverage would be increased close to 100%, 93% of diarrheal deaths could be prevented.xi
We will expect in more detail at the specific prevention and handling measures against diarrheal diseases in upcoming posts. This should assist to make clear what is possible and effective in preventing and treating one of the leading causes of decease in children.
Potential of interventions to forbid the burden of diarrheal diseases in childhood12
| Intervention | Estimate of the result size |
|---|---|
| Handwashing with soap | 48% adventure reduction |
| Improved h2o quality | 17% take chances reduction |
| Excreta disposal (improved sanitation) | 36% risk reduction |
| Breastfeeding education | 43% increment in sectional breastfeeding rates at 24-hour interval 1, xxx% increase until 1 month, and 90% increase from ane-6 months |
| Preventive zinc supplementation | 13% reduction in diarrhea incidence, but no effect on mortality |
| Therapeutic zinc supplementation | 46% reduction in all-cause mortality and 23% reduction in hospitalization due to diarrhea |
| Rotavirus vaccines | 74% effectiveness against very astringent rotavirus infection; 61% against astringent; 47% reduction in hospitalization |
| Cholera vaccines | 52% constructive against cholera infection |
| Oral rehydration solution (ORS) | 69% reduction in diarrhea-specific mortality |
| Dietary management for diarrhea | 47% reduction in diarrhea treatment failure and 47% reduction in handling failure |
| Antibiotics for cholera | 63% reduction in clinical failure rates |
| Antibiotics for Shigella | 82% reduction in clinical failure rates |
| Antibiotics for cryptosporidiosis | 52% reduction in clinical failure rates |
| Community-based interventions (home visits and healthcare promotion) | 160% increment in ORS employ and 80% increment in zinc use. 9% increase in seeking care for diarrhea and 75% reduction in inappropriate antibiotic utilise |
Source: https://ourworldindata.org/childhood-diarrheal-diseases
0 Response to "Please Die, You Dying Babies, in My Diarrhea."
Postar um comentário